Benefits of the Open Standard MQTT in the Wastewater Industry
According to Edward Jones, PhD researcher at Utrecht University and a leading authority in water and wastewater research, about 359 billion cubic meters of wastewater is produced globally each year, equivalent to 144 million Olympic-sized swimming pools. Worldwide, it is common practice to pump enormous volumes of wastewater into rivers, oceans, and streams. The practice has extremely negative effects on the environment, fisheries, and animals — not to mention that it’s an aptly named ‘waste’ of water too. Wastewater treatment is crucial for protecting our environment and ensuring that we make the most efficient use of our resources. The treatment impacts every country, state, city, county, municipality, and village in the world as access to clean drinking water is a basic human necessity.
Let’s explore some of the issues faced by the wastewater industry, how IoT helps address these issues, and finally the role played by MQTT in enabling IoT use cases.
Challenges Faced by the Wastewater Industry
The wastewater industry faces several challenges ranging from environmental concerns to infrastructure and management issues. Some of the key challenges include:
Aging Infrastructure
Much of the water and wastewater infrastructure in many countries is aging and in need of repair or replacement. Aging infrastructure leads to leaks, breaks, and inefficiencies, resulting in water loss and potential contamination of water sources.
Water Pollution
Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and improper disposal of waste contribute to water pollution. Contaminants such as chemicals, heavy metals, pathogens, and nutrients can degrade water quality, posing risks to human health and ecosystems.
Energy Consumption
Water and wastewater treatment processes require significant energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and operating costs. Finding ways to reduce energy consumption and improve energy efficiency is essential for sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Addressing these issues requires collaboration among governments, utilities, industry stakeholders, and the public, as well as investment in research, technology development, and infrastructure improvement.
How IoT Technology Can Address Some of the Challenges
IoT (Internet of Things) technology plays an important role in addressing the various challenges in the wastewater industry by providing real-time asset monitoring, data analytics, and automation capabilities.
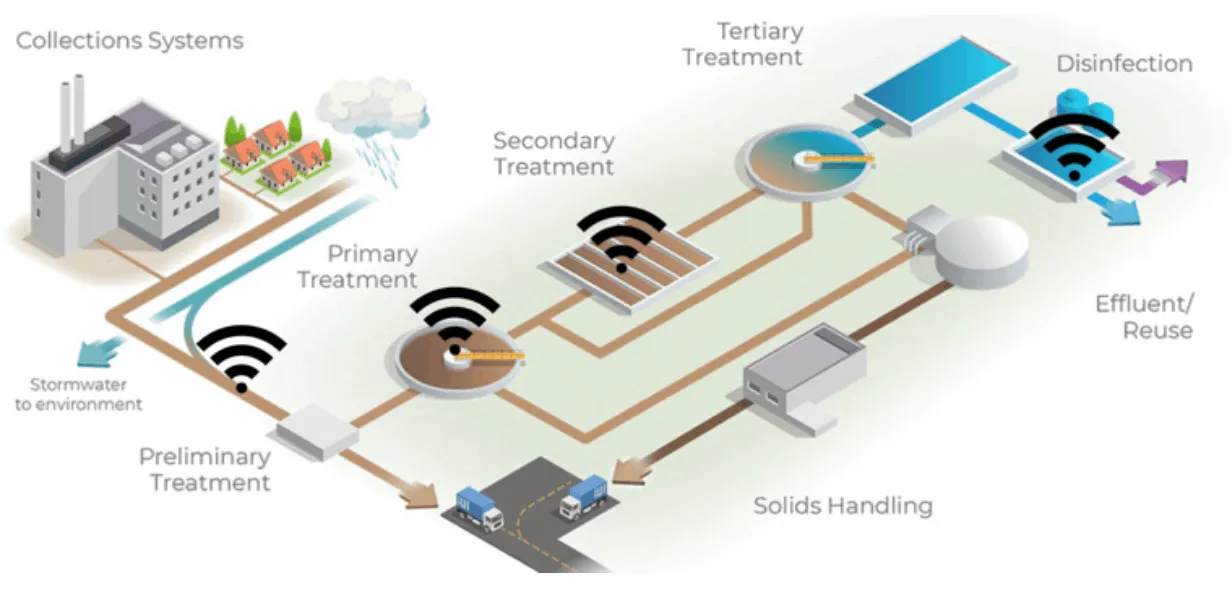 IoT in Water Treatment plants: Source: https://blog.temboo.com/iot-and-wastewater-treatment-plants/
IoT in Water Treatment plants: Source: https://blog.temboo.com/iot-and-wastewater-treatment-plants/
Here are some ways IoT helps address key challenges:
Predictive Maintenance
By continuously monitoring equipment conditions and performance metrics, IoT-enabled predictive maintenance systems can predict when equipment is likely to fail or require maintenance. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of critical infrastructure components.
Water Quality Monitoring
IoT sensors can monitor various parameters such as pH, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, and chemical concentrations in real-time. This enables early detection of contaminants or abnormalities, allowing water utilities to take prompt corrective actions to maintain water quality and comply with regulations.
Leak Detection and Water Loss Management
IoT devices equipped with leak detection sensors can identify leaks in water distribution networks quickly. By pinpointing the location of leaks and monitoring flow rates, utilities can minimize water loss, conserve resources, and improve efficiency.
Overall, IoT technology empowers water and wastewater utilities to enhance operational efficiency, improve resource management, ensure regulatory compliance, and deliver better services to customers and communities.
How MQTT Enables IoT Data Availability to Support Water and Wastewater Management
MQTT is a lightweight messaging open standard protocol used in IoT for data movement and is designed for efficient communication between devices in low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unreliable networks. In the wastewater industry, MQTT can help address various IoT data challenges by facilitating real-time data exchange, remote monitoring, and control.
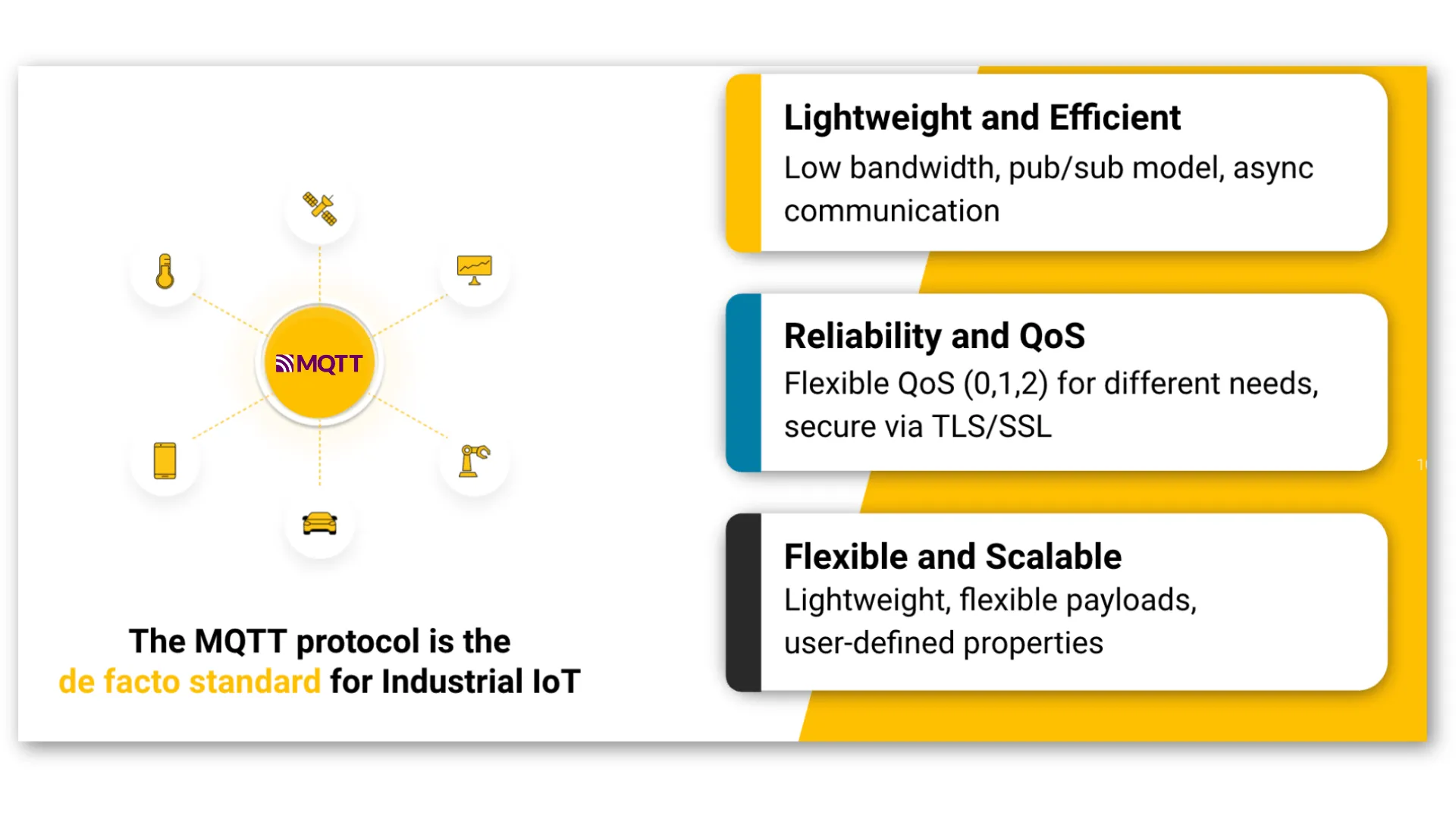 Here's how MQTT helps:
Here's how MQTT helps:
Real-Time Monitoring:
MQTT enables real-time transmission of sensor data from various points in wastewater systems to centralized monitoring systems. This is possible because it is an event-driven architecture and provides the most up-to-date data in real time. This allows operators to continuously monitor parameters such as water quality, flow rates, pressure levels, and equipment status, facilitating timely detection of abnormalities or issues. The HiveMQ solution is helping LEC in its goal of reducing or eliminating water waste for their customers by enabling leak detection, remote monitoring control capabilities for wells, pumps, motors, and water usage systems.
Scalability and Flexibility:
MQTT's lightweight and efficient nature make it well-suited for large-scale deployments across distributed wastewater infrastructure. It supports a publish-subscribe messaging model, allowing multiple clients to subscribe to relevant data topics without placing undue burden on network resources. HiveMQ offers advanced scalability features and has benchmarked up to 200M active clients.
Reliability and Resilience:
MQTT’s publish/subscribe architecture and support for Quality of Service (QoS) levels ensure reliable message delivery even in challenging network conditions or intermittent connectivity. This reliability is critical for maintaining continuous monitoring and control of water and wastewater systems, especially in remote or harsh environments. HiveMQ delivers IoT data with enterprise-grade reliability for mission-critical applications.
Data Integration and Interoperability:
MQTT facilitates seamless integration with existing SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), DCS (Distributed Control Systems), PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), and IoT systems commonly used in water and wastewater facilities. It enables interoperability between diverse devices and platforms, ensuring smooth data exchange and system optimization. HiveMQ Edge offers device drivers that can convert some of the common machine protocols into MQTT and helps package IoT data to be shared with the enterprise for advanced analytics.
Security:
MQTT supports various security mechanisms such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) and authentication mechanisms, ensuring secure communication and data integrity. This is crucial for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access or tampering with water and wastewater systems. HiveMQ offers an enterprise-grade broker with advanced security features.
Edge Computing:
MQTT can be combined with edge computing platforms to perform data preprocessing, analysis, Edge AI and decision-making at the edge of the network. This reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and enables faster response to critical events or alarms in water and wastewater systems.
MQTT: An Open Standard That Has Revolutionized Wastewater Management Processes
MQTT plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency, reliability, and resilience in wastewater operations by enabling real-time monitoring, remote control, data integration, and automation. Its open standard, lightweight, scalable, and interoperable nature makes it well-suited for addressing the complex challenges faced by the industry. It enables IoT solutions in wastewater to optimize operations and enhance safety. In Part 2 of this blog series, we will discuss in detail how HiveMQ enables wastewater industry customers such as LEC in the US and Anglian Water in the UK to achieve their IoT use cases such as remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and others.
Stay tuned to Part 2 where we profile what some of our real-world customers are doing in the wastewater industry. Meanwhile, explore our use cases across different industries.

Ravi Subramanyan
Ravi Subramanyan, Director of Industry Solutions, Manufacturing at HiveMQ, has extensive experience delivering high-quality products and services that have generated revenues and cost savings of over $10B for companies such as Motorola, GE, Bosch, and Weir. Ravi has successfully launched products, established branding, and created product advertisements and marketing campaigns for global and regional business teams.
