What are MQTT User Properties? – MQTT 5 Essentials Part 6
Welcome to Part 6 of our MQTT 5 Essentials series. In Part 5, we delved into the realm of improved Client Feedback and Negative Acknowledgements, shedding light on how they enhance the functionality of the MQTT system. In this article, we guide you through another groundbreaking feature: User Properties. This addition is poised to revolutionize how you interact with MQTT, creating a more customized and insightful user experience.
In essence, User Properties are the user-defined properties that help you add metadata to MQTT messages and help transmit additional user-defined information.
Let’s dive in.
MQTT 5 has been meticulously crafted to bridge the existing chasm between the offerings of MQTT 3.1.1 and the evolving expectations of users from this de facto standard protocol for the Internet of Things. With MQTT 5, we’re ensuring that MQTT continues to lead the pack as the IoT protocol par excellence for many more decades.
How User Properties in MQTT 5 Work?
In MQTT 5, User Properties fundamentally operate as straightforward UTF-8 string key-value pairs. Their utility lies in their ability to be affixed to nearly every category of MQTT packet, with the sole exceptions of PINGREQ and PINGRESP. This broad application extends to various control packets like PUBREL and PUBCOMP.
The power of User Properties is in their uncapped potential - as long as the maximum message size isn’t exceeded, you are free to employ an infinite number of User Properties. This opens up vast possibilities for enriching MQTT messages with additional metadata, facilitating a fluid transmission of information between the publisher, broker, and subscriber.
Conceptually, this feature closely mirrors the role of headers in HTTP. It’s this resemblance that allows User Properties to inject a level of customizable complexity into MQTT 5, helping to create a protocol that is not only more robust but also more adaptable to user needs.
Why Were User Properties Introduced in MQTT 5?
MQTT 3 users identified two significant limitations: the protocol’s constrained extensibility and the complexity of creating multi-vendor deployments. To rectify these concerns, MQTT 5 introduced the User Properties feature, effectively mitigating these challenges.
User Properties provide an avenue for enhancing flexibility by enabling users to transport virtually any piece of information across the entire MQTT system. This capability ensures that the MQTT protocol no longer restricts but promotes customized enhancements. This leap forward in functionality paves the way for users to augment standard protocol features, tailoring them to meet their specific requirements.
In doing so, MQTT 5 ensures that the protocol evolves in step with its users, facilitating greater adaptability and easing the integration of multi-vendor deployments.
Practical Use Case Examples of MQTT 5 User Properties
While the intricacies of the User Properties feature might initially seem minor, the practical implications of possessing a mechanism to transfer metadata across the complete MQTT ecosystem are indeed substantial. To illustrate this transformative potential, let’s delve into three common use cases that underscore the need for a feature like User Properties—a need articulated repeatedly by users eagerly awaiting the introduction of this component in the MQTT specification.
Saving Resources with Payload Metadata Using User Properties in MQTT 5
In environments where MQTT serves as a connector between diverse systems developed by different teams or vendors, variability in payload structures is quite commonplace. Clients may transmit data in many formats, including JSON, XML, or compressed formats such as Protobuf.
The advent of User Properties in MQTT 5 opens the door to appending metadata to messages, encapsulating specific details such as the markup language and version employed to encode the payload. This metadata provision obviates the need for the receiving client, or in certain instances, the broker, to unpack the payload and cycle through an array of possible parsers until the appropriate one is located.
Instead of this cumbersome process, each message arrives equipped with its parsing information, streamlining interpretation and significantly reducing the computational load across the entire system. This efficient use of resources amplifies the overall performance and speed of the MQTT network, showcasing the transformative power of User Properties.
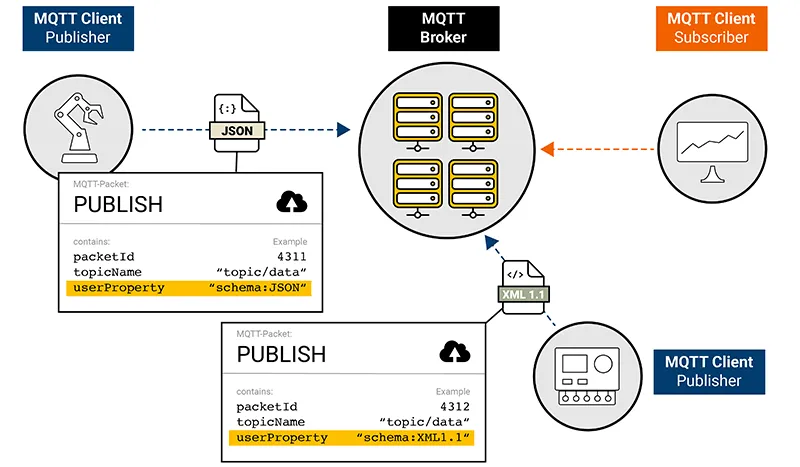
Including metadata about the used markup language in the payload can significantly relieve the system.
Increased Efficiency Through Application Level Routing Using User Properties in MQTT 5
With its data transportation and routing proficiency, MQTT frequently serves as the backbone for large-scale data processing and streaming deployments. Such deployments typically involve a multitude of devices, systems, and applications. It’s quite common for different systems to receive identical messages but for distinct purposes. For instance, one system may display live data while other archives the same data for long-term storage.
In such scenarios, User Properties can prove invaluable by serving as an additional application-level timestamp for the message. This attribute lets the broker quickly ascertain whether certain messages should not be passed to a specific subset of subscribers based on a predefined validity period. This feature introduces an added application-level layer that further refines message relevance according to the Message Expiry Interval.
Therefore, User Properties in MQTT 5 not only bolster the system’s efficiency but also provide a finer level of control, thereby maximizing the utility and relevancy of each transmitted message.
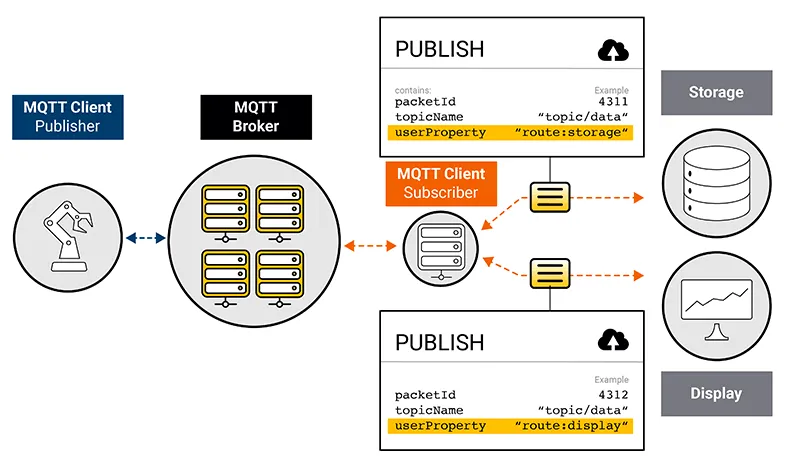
Example: user properties provide information for the broker, if messages should be routed to a storage or a display application.
Transparent Traceability in Complex Systems Using User Properties in MQTT 5
The landscape of IoT deployments often presents a maze of intricacy, with individual systems operating in parallel. Such complexity can cloud the origin of a specific message or the factors contributing to an unsuccessful multi-layer message flow. Under the MQTT 3.1.1 framework, there was no mechanism for a subscriber to discern the identity of a message’s publisher. Although embedding a unique identifier in the topic is a viable strategy in 1-to-1 scenarios, this approach undermines several pivotal advantages of the publish-subscribe model.
In this regard, the advent of the User Property feature in MQTT 5 heralds a significant transformation. This innovative addition enables publishers to effortlessly include relevant self-identifying information, such as a client ID or the region where the publishing is conducted. Importantly, this information is relayed to all message recipients without necessitating any supplemental business logic.
Incorporating information about the publisher’s region enhances the system’s traceability while attaching a unique system identifier to MQTT messages enables comprehensive logging and tracking of the entire message flow from the sender to all subscribers. Implemented effectively, these identifiers can extend across multiple MQTT message flows, introducing unprecedented transparency and traceability.
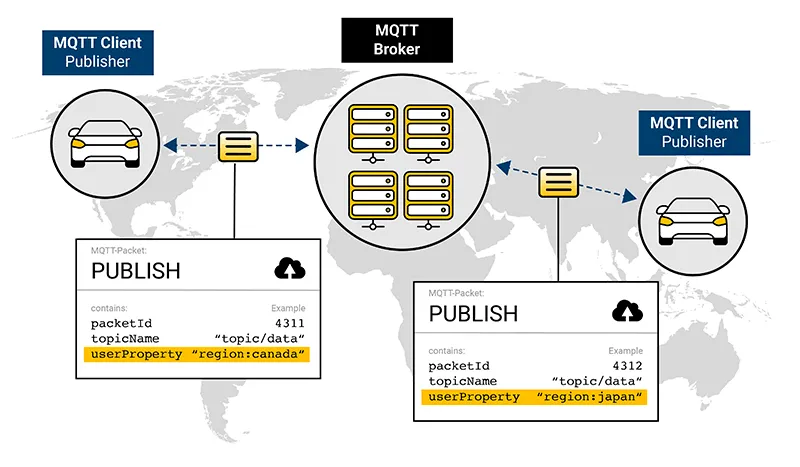
Adding information about the publishers region adds traceability to the system.
Such capabilities unlock a new horizon of possibilities, particularly for business-critical applications like premium paid services for end customers, where transparency and traceability become indispensable.
Summary and Additional Information on User Properties in MQTT 5
User properties serve as UTF-8 string key-value pairs that can seamlessly be incorporated into any MQTT message. This ability positions them as versatile and invaluable addition to the MQTT protocol.
The potential for implementing User Properties in enhancing MQTT use cases is practically boundless. It offers a degree of customization that allows for many innovative applications, both in function and scope.
Deployments and projects that extend over multiple systems and vendors can leverage this feature to maintain consistency and ensure seamless communication across the entire infrastructure.
We are exhilarated to see the myriad of inventive ways MQTT users will harness the potential of this deceptively simple yet impactful feature.
User Properties in MQTT 5 represent a significant step forward in protocol extensibility and versatility, opening up exciting possibilities for future IoT applications.
Learn More About MQTT 5
That’s the end of Part 6 in our MQTT 5 Essentials series. We hope that you find this information useful. In Part 7 of this series, we’ll shed light on the intriguing concept of Shared Subscriptions.
Sign up for our newsletter to get regular updates. Subscribe to our RSS feed here to stay updated. We encourage you to visit our MQTT Glossary for an in-depth understanding of the essential MQTT terminologies. It will equip you with the necessary vocabulary to grasp the complexities of MQTT and its various versions. Watch the video below that complements the concepts discussed in this article.
Watch the Video
Chapters
- 00:00 - Welcome
- 00:15 - User Properties in MQTT5
- 00:46 - Typical use cases for User Properties in MQTT5
- 02:04 - Conclusion and announcing part 6 - Shared Subscriptions in MQTT5

