Achieving IT/OT Convergence with MQTT, UNS, and HiveMQ
As the industrial landscape evolves, the convergence of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) has become crucial for driving efficiency, resilience, and digital transformation. According to McKinsey & Company, organizations that effectively integrate IT and OT can unlock significant value, potentially adding up to more than $100 million in incremental benefits through improved operations and decision-making capabilities.
HiveMQ bridges Industrial IoT data into the enterprise, removing silos and enabling seamless integration using its MQTT-based platform. This blog explores how HiveMQ, MQTT, and UNS work together to achieve IT/OT convergence.
A Four-Step Roadmap to IT/OT Integration
Many of our customers follow the four steps shown in Image 1 to achieve IT/OT convergence using MQTT and the UNS framework with data modeling, conceptualization and consolidation. Each numbered section in the diagram below represents a step in this process, starting from IIoT connectivity and progressing through to the digital supply chain and beyond. These four steps help organizations bridge the gap between IT and OT systems. Let’s explore each step in detail.
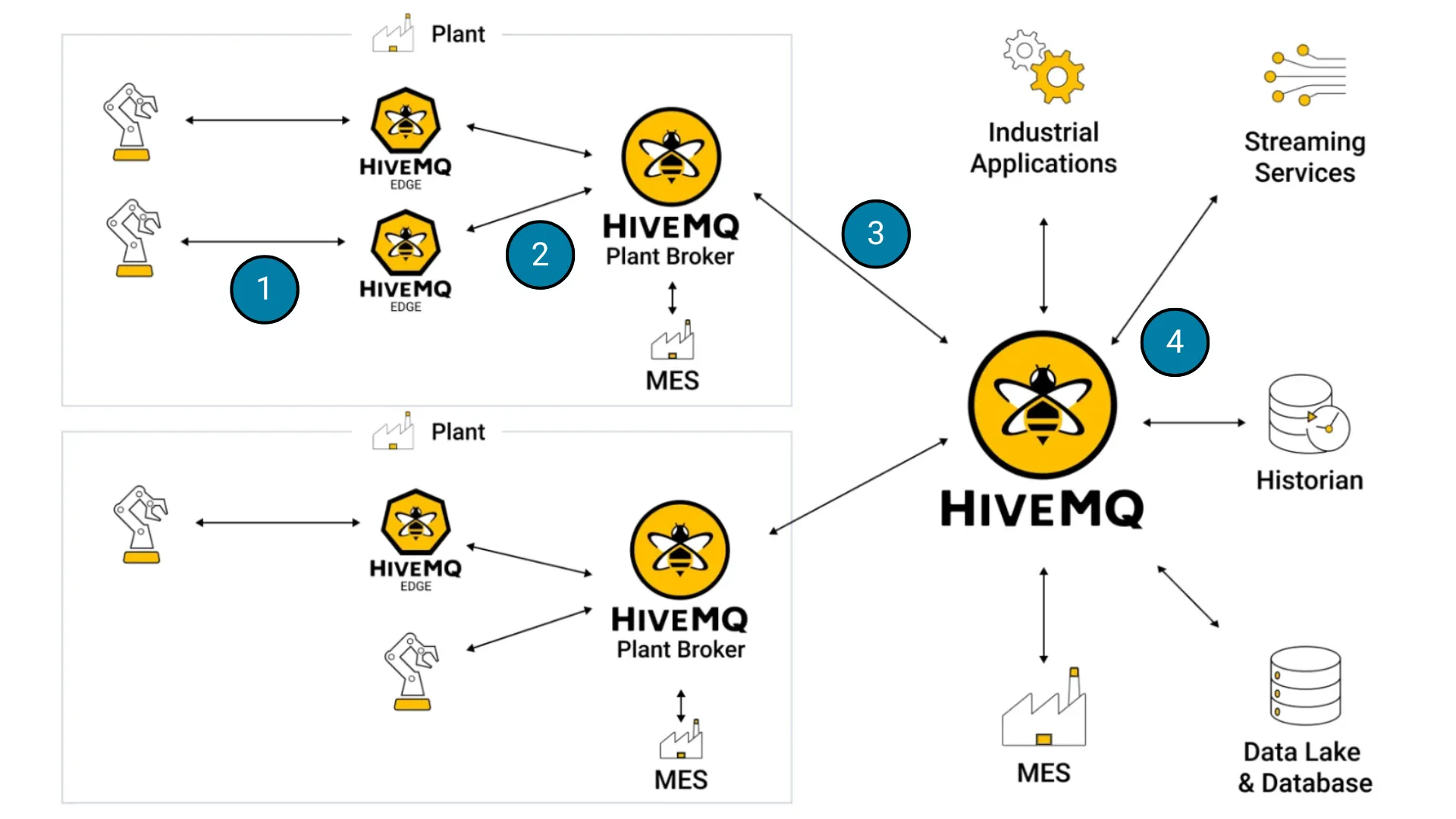 Image 1: A visual representation of the four steps to achieve IT/OT convergence
Image 1: A visual representation of the four steps to achieve IT/OT convergence
Step 1: Connecting Devices at the Edge
Integrating devices and gateways at the edge is the first step toward a connected industrial framework. IIoT gateways like HiveMQ Edge convert IIoT protocols to MQTT, enabling devices to efficiently report by exception and transmit data seamlessly. Connecting the local HiveMQ Edge to a HiveMQ plant broker provides scalable, real-time OT connectivity.
As data is connected at the edge, collecting metadata becomes crucial for defining its organization and payload format, enabling deeper insights. Typically customers use their own data frameworks to support that metadata management. While there are existing frameworks like OPC UA and Sparkplug, they may not be completely suitable for the use cases where customers have to share the data from OT to IT systems.
Sparkplug, a specification that works on top of MQTT, does offer some features like topic namespace definition, payload definition and state management. HiveMQ is fully compatible with Sparkplug and supports the latest Sparkplug specification. In scenarios where the edge data needs to be integrated with other enterprise data, Sparkplug may present challenges, as it is primarily designed as a framework for OT machine data.
Once devices are connected at the edge, the next focus is on integrating these edge systems with plant-level infrastructure to build a cohesive data flow.
Step 2: Bridging Edge to Plant Systems
The MQTT protocol has become an industry standard for its efficiency and real-time capabilities. If you’re an OT professional looking to understand why MQTT is vital for IT/OT integration, read our blog Explaining to OT Teams the Importance of MQTT for IT/OT Interoperability.
Leveraging local MQTT connectivity solutions like HiveMQ Edge, which bridge the data from the edge to a local or plant-level broker, businesses can create agility at the edge by decoupling local system interactions. This setup incorporates data from diverse devices and sensors, enabling seamless data consolidation at the local or plant level with native MQTT support.
HiveMQ Edge ensures no data is lost during outages by buffering data locally and seamlessly resuming data flow once connectivity is restored. Adding UNS aliases to edge data provides meaningful context, simplifying interpretation and analysis. Additionally, HiveMQ Data Hub enables data cleansing and quality management at the source, ensuring that only the right data flows through to receiving systems. Time-series data publishes directly to local historians and databases at the local or plant level, enriching analytics and operational insights.
With edge-to-plant data consolidation in place, the next step is ensuring secure and seamless data exchange across centralized systems.
Step 3: Establishing Secure Central Connectivity
A seamless IT/OT interface requires bridging local and/or plant brokers to central brokers. This enables bi-directional connectivity using outbound MQTT connections and facilitates secure, continuous data flow without the complexities of direct incoming connections to local networks. This method overcomes significant security and provisioning challenges, reducing associated costs and administrative burdens.MQTT message queues safeguard against intermittent connectivity issues, ensuring continuous data flow. It is also possible to add additional layers, such as bridging from a site/plant/local broker to a DMZ broker and then to the cloud, enhancing security and control over data flow.
After establishing secure central connectivity, a Unified Namespace (UNS) acts as the foundation for enabling enterprise-wide data access and analysis.
Step 4: Creating a Unified Namespace
A centralized UNS, as shown in Image 2 below, acts as the backbone of IT/OT convergence, enabling bi-directional, near-real-time data exchange. It acts as the single source of truth for all industrial business data. It enables the various industrial users to see the state of the business at any given point in time. It acts as a single source of truth, ensuring IT business applications have consistent and reliable data. This enables visualization, analysis, and advanced analytics of the IIoT data and assets, facilitating effective decision-making and proactive operational control.
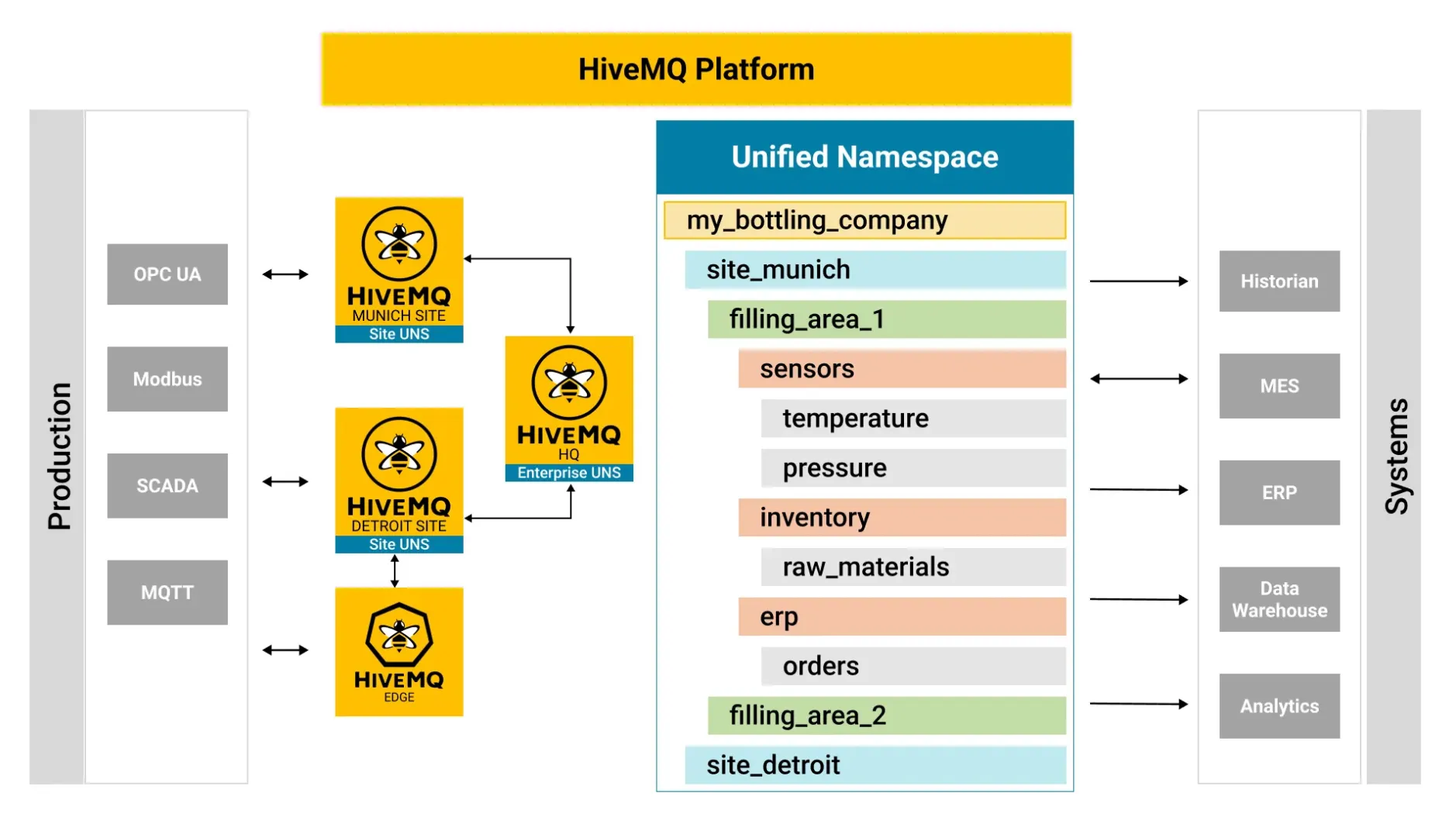 Image 2: A visual representation showing a Unified Namespace that enables IT/OT convergence
Image 2: A visual representation showing a Unified Namespace that enables IT/OT convergence
Scaling with Data Streaming and Enterprise Systems
As organizations scale their IoT ecosystems, the need for streaming and real-time processing becomes essential. The HiveMQ MQTT platform can support data streaming use cases with its on premise or cloud based solutions. If there is a need to integrate with Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis, Azure Event Hubs, Data Lakes, Databases or other data sinks to perform advanced analytics, AI/ML, and Big Data applications, HiveMQ provides integrations to bridge the MQTT data into those platforms.
Transforming the Digital Supply Chain
A truly connected digital supply chain is one that integrates various assets and stakeholders through a standard, distributed interface. MQTT, with its publish/subscribe architecture, facilitates near real-time collaboration across remote devices and systems, enhancing the efficiency of supply chain and logistics operations. Extending connectivity to partners, regulators, and external systems bridges the gap between internal networks and broader ecosystems, fostering collaboration. This approach supports digital transformation efforts by ensuring streamlined, synchronized operations across the entire supply chain.
Conclusion
Achieving IT/OT convergence involves creating an agile, scalable, and secure data architecture that promotes real-time collaboration and decision-making. With MQTT as the communication standard, HiveMQ as the central hub, and UNS as the integrative layer, enterprises can overcome connectivity and integration challenges, ultimately moving toward a fully connected, digital-first business model.
With these tools and strategies, your organization can unlock the full potential of IT/OT convergence. Discover how HiveMQ can support your journey by exploring our solutions or connecting with our experts.

Ryan Dussiaume
Ryan Dussiaume, a Solutions Engineer at HiveMQ, combines his software development expertise with a passion for staying at the forefront of technology. Proficient in IIoT, MQTT, and UNS, Ryan is dedicated to guiding companies on their Industry 4.0 transformation, leveraging his experience with middleware and cloud native technologies to benefit individuals, teams, and businesses.

Ravi Subramanyan
Ravi Subramanyan, Director of Industry Solutions, Manufacturing at HiveMQ, has extensive experience delivering high-quality products and services that have generated revenues and cost savings of over $10B for companies such as Motorola, GE, Bosch, and Weir. Ravi has successfully launched products, established branding, and created product advertisements and marketing campaigns for global and regional business teams.
