Advancing Digital Twin Use Cases with IIoT and MQTT
Digital twin technology has revolutionized the industrial sector by giving companies the power to mirror almost every facet of a product, process, or service. Digital twins have the potential to replicate everything in the physical world in the digital space and provide industrial users with feedback to drive better decisions. The technology enables companies to quickly detect and solve physical problems, design and build better products, and realize value and benefits faster than previously possible.
A digital twin is a virtual model designed to accurately reflect a physical object. The object being studied, like a wind turbine or injection molding machine, is outfitted with various sensors related to vital areas of functionality. These sensors produce data about different aspects of the physical object’s performance, such as energy output, temperature, weather conditions and more. This data is then relayed to a processing system and applied to the digital copy.
Gartner estimates that by 2027, over 40 percent of large companies worldwide in the industrial sector including manufacturing, energy, transportation and others will be using digital twins in their projects to increase revenue, reduce costs, and improve operations.
How Does Digital Twin Technology Work?
The three main aspects of digital twins are data acquisition, data modeling, and data application. Digital twins use four technologies to collect and store real-time data, obtain information to provide valuable insights, and create a digital representation of a physical object.
These technologies include the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Extended Reality (XR), and Cloud. In addition, digital twins use a particular technology, depending on the application type and use case.
 The Digital Twin Ecosystem | Image Source: sciencedirect.com
The Digital Twin Ecosystem | Image Source: sciencedirect.com
Industrial Use Cases for Digital Twins
Here are three key applications of digital twins for industrial use cases:
1. Monitoring and Analysis
The digital twin is continuously updated with new data from the physical asset, which allows for real-time monitoring and analysis. Engineers, operators, and industrial decision-makers can use the digital twin to gain insights into the performance, health, and efficiency of the physical asset. For instance, predictive maintenance can be performed by analyzing historical data and making predictions about when maintenance is required.
2. Remote Control and Optimization
With a digital twin in place, industrial operators can make changes and adjustments to the virtual model. These changes can then be tested before being applied to the physical asset.
This capability enables remote control and optimization of industrial processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
3. Simulation and Scenario Planning
Digital twins also allow for simulations and scenario planning. Industrial operators can simulate various conditions or scenarios and assess how they would impact the physical asset or system. This is invaluable for decision-making and risk assessment.
Data Acquisition and Connectivity to Enable Digital Twins
For industrial data acquisition and connectivity, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and the MQTT protocol play key roles in enabling digital twin use cases, which are essential for improving efficiency, monitoring, and decision-making in various industries.
IIoT involves connecting industrial devices, systems, and applications to the enterprise to move real-time data. These devices could be equipped with sensors, actuators, and others to make them connected devices that can collect and transmit data in a standard format like MQTT.
MQTT is a lightweight publish- subscribe-based messaging protocol that was developed specifically to handle the unique requirements of IIoT connections. It excels in constrained environments where network bandwidth is limited. It enables IIoT systems to collect data from various disparate systems and publish data to a centralized system also known as a broker. The broker (for instance HiveMQ as shown in the diagram below) then enables the data to be shared with other systems typically on the enterprise network in real time.
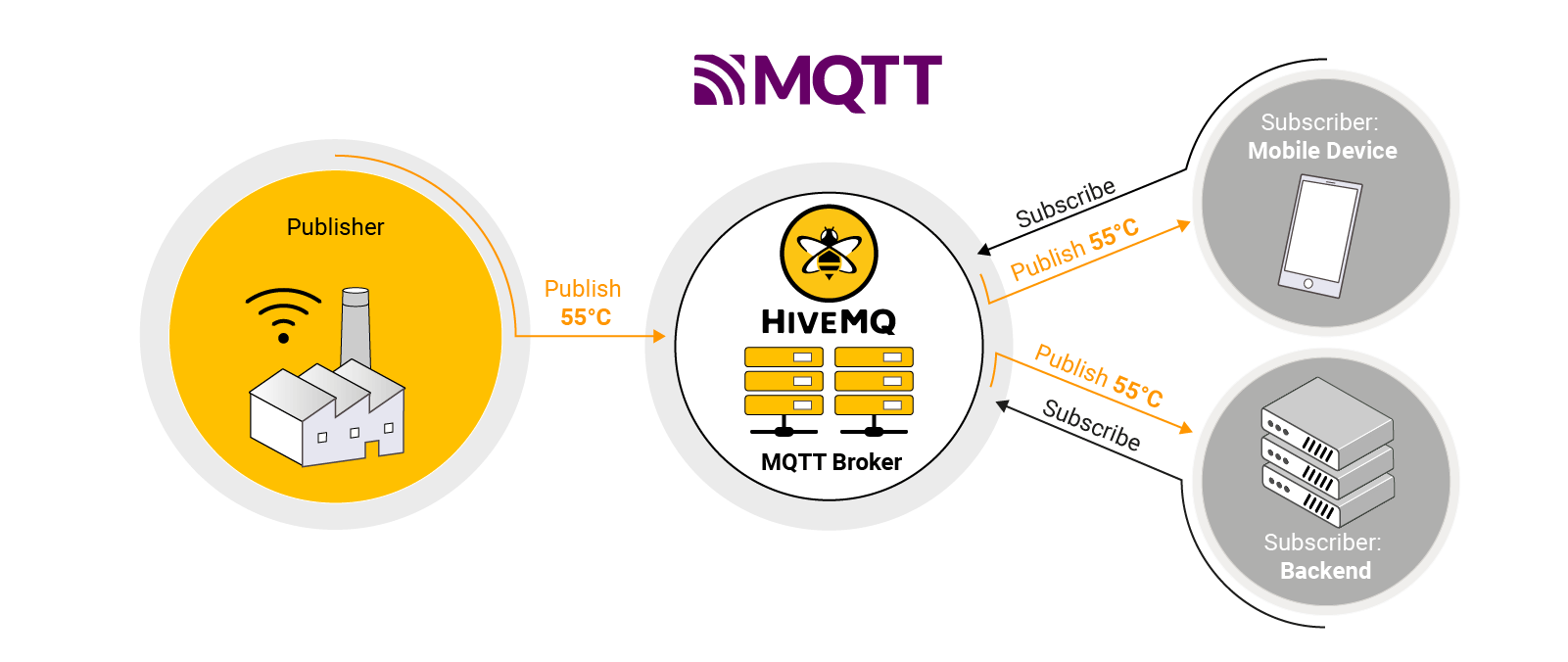
This real-time data exchange is crucial for digital twins as it ensures that the digital replica is constantly updated with the latest information from the physical assets.
Data Integration and Processing
Data collected from IIoT systems through an MQTT broker is sent to cloud-based or on-premises systems where it can be processed and analyzed. An MQTT data broker is able to augment the IIoT system data with relevant data from other sources like Historians, MES, ERP, and other external systems. The broker then creates a single source of truth that is then used to create and update the digital twin model, which is a virtual representation of a physical asset or system. The model includes information about the asset’s current state and historical data.
IIoT and MQTT provide the necessary infrastructure and communication capabilities to gather real-time data from industrial assets, which is essential for creating and maintaining digital twins. These technologies facilitate data exchange, analysis, and decision-making, leading to improved operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and better overall performance in various industries.
How Does HiveMQ Enable Digital Twins?
HiveMQ is the leading enterprise MQTT platform that simplifies the process of collecting device data through its HiveMQ Edge solution, ensures that the data is high quality through its Data Hub solution, and also offers an enterprise-grade data broker to enable digital twin use cases. It streamlines the connection between OT systems and the cloud, ensuring scalable, reliable, secure, and real-time communication. With its Sparkplug compatibility, HiveMQ ensures that industrial data tags are automatically discovered and available in the cloud to enhance the digital twin applications. HiveMQ’s robust and scalable architecture makes it the ideal solution for managing IIoT data in an industrial environment.

Digital Twins Enable Companies to Go from Reactive to Predictive
Digital twins are a power tool enabled by various technologies including IoT, AI, Cloud computing, and XR. An MQTT broker is the key enabler for data connectivity, acquisition and providing the single source of truth to enable digital twin applications. By utilizing the power of the digital twin, industrial companies can move from being reactive to predictive. They can predict when equipment is wearing down or needs repair, improve the machine’s performance, extend their lives and learn how to redesign to do even more. Given its robust nature, there could be many more applications of digital twins that will be developed in the years to come. As technology enablers keep getting more advanced and accessible, they will enable digital twins to be used in many newer applications that will further optimize operations and lead to more profitability for industrial companies.
To learn more and get started, check out our Smart Manufacturing white paper.

Ravi Subramanyan
Ravi Subramanyan, Director of Industry Solutions, Manufacturing at HiveMQ, has extensive experience delivering high-quality products and services that have generated revenues and cost savings of over $10B for companies such as Motorola, GE, Bosch, and Weir. Ravi has successfully launched products, established branding, and created product advertisements and marketing campaigns for global and regional business teams.
