Enabling Data Insights from Industry 4.0 in Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 represents a significant shift in manufacturing, driven by technological advancements. By leveraging these technologies, manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency, improved quality, better customization, greater flexibility, enhanced innovation, and reduced costs.
Key Technologies Driving Industry 4.0
Internet of Things (IoT)
Sensors and Connectivity: Devices equipped with sensors and connectivity that collect and share data with data brokers, which in turn consolidate and make data available to IT systems for analytics.
Real-Time Monitoring: Enables real-time monitoring and analysis of production processes.
Big Data and Analytics
Data Collection: Massive amounts of data are collected from various sources.
Predictive Analytics: Analyzing data to predict maintenance needs, optimize production, and reduce downtime.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Automation and Robotics: Smart robots and automated systems that learn and adapt over time.
Decision Support Systems: AI-driven systems that assist in decision-making processes.
Advanced Robotics
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Robots that work alongside human workers.
Autonomous Robots: Robots that can perform tasks without human intervention.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Prototyping and Production: Rapid prototyping and small-batch production using 3D printing technologies.
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
Integration of Physical and Digital Systems: Creating systems where physical processes are monitored and controlled by computer-based algorithms.
Cloud Computing
Data Storage and Processing: Storing and processing data on remote servers to enable scalability and flexibility.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Accessing software applications over the internet.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Training and Maintenance: Using AR and VR for training, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Design and Simulation: Enhancing design and simulation processes.
Challenges and Opportunities with Industry 4.0 Technologies
These technological transitions also present challenges like cybersecurity, skill gaps, integrations, data management, and ROI justification that need to be addressed to fully realize the benefits of this industrial revolution.
To understand the needs of manufacturers, The Manufacturer magazine ran a survey in 2024 of its over 250,000 manufacturing community members and published their findings in a report named “Manufacturing Momentum Report 2024” which presented a comprehensive overview of commercial opportunities within the manufacturing sector. Interestingly, some of the areas covered in the findings as opportunities are also seemingly some of the challenges mentioned above.
Let us explore some of the insights gained in those areas.
Artificial Intelligence
The manufacturing sector is expected to continue to undergo significant transformations in 2024. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of it with increasing adoptions across various applications, including production, decision-making, and operational efficiency. Responses to the survey suggest that traditional methods of managing processes are seen as limited, and AI, particularly machine learning (ML), is highlighted as a solution that can adapt to the increasing complexity and unpredictability of modern manufacturing. When asked the question about challenges with AI (Fig. 1), 14% of manufacturers stated data issues, and 63% were not sure where to start.
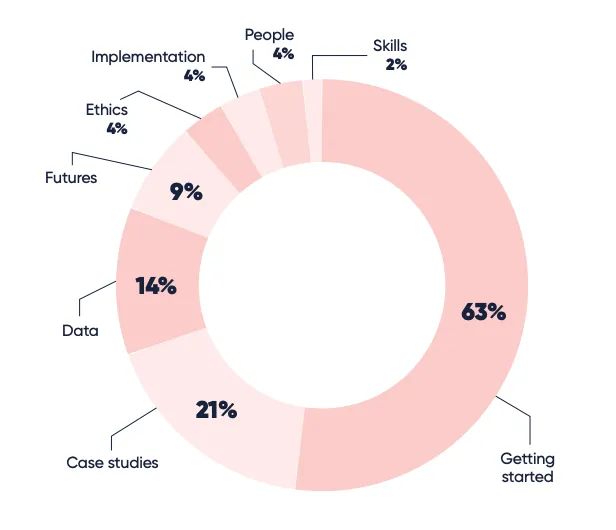
Fig. 1: What are the challenges you face with AI?
Focusing on the getting started part, the biggest challenge manufacturers face is integrating legacy systems spread across various areas, cells, lines, and sites in manufacturing to enable AI. These could need a lot of retrofitting to ensure that these systems can be connected, bandwidth can be improved, and connectivity can be stabilized—all of which could be a sizable investment. Companies struggle with the ROI of these investments at the get-go as the technology is not proven yet.
The best practice in such scenarios is to ensure that the business objectives are aligned with AI, opportunities for AI are identified, AI use cases are defined, and company culture is aligned with the use of AI. This would then justify the investment costs. Using proven Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technology like MQTT to enable data movements; Edge Technology to capture and consolidate the data from the various manufacturing systems helps streamline the process and set up AI for success. HiveMQ is the industry-leading enterprise-grade MQTT broker and edge gateway provider with proven success in enabling manufacturers to future-proof their AI investment. HiveMQ Edge enables interoperability between the various OT and the various IT systems by translating diverse machine protocols into standardized formats, modernizing IoT infrastructure, and making seamless edge-to-cloud integration a reality. HiveMQ enterprise broker provides an event-driven messaging platform that’s designed for the fast, efficient, and reliable movement of data between Operations Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) systems.
Data
Manufacturing is considered the most data-intensive industry, generating an average of 1.9 petabytes of data annually. Naturally harnessing all this data to make it insightful is absolutely important for manufacturers to drive value.
When asked about where they are with their manufacturing data, only 11% of manufacturers responded that they are currently choosing technology providers in the Industrial Data and Analytics space. Also, the broad landscape of challenges in managing data within a manufacturing business is highlighted by the range of responses.
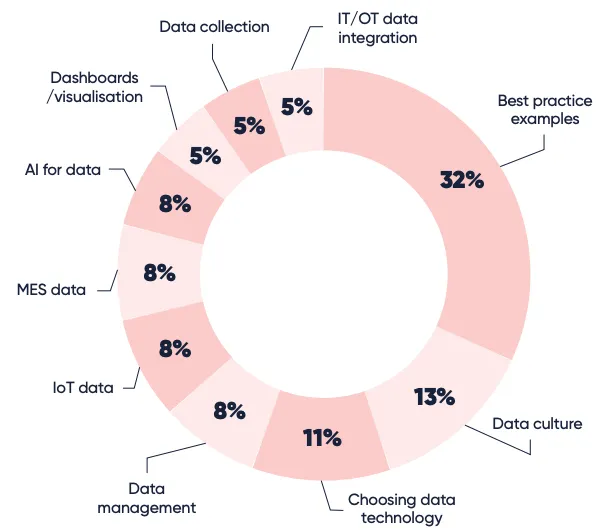 Fig. 2: What are some of the challenges with data and how do you use data from manufacturing?
Fig. 2: What are some of the challenges with data and how do you use data from manufacturing?
Good data is at the forefront of all the Industry 4.0 use cases, which drive value for manufacturing. However, there are a lot of challenges with data collection, data consolidation, normalization, cleansing, and contextualization—all vital to power some of the advanced use cases like Digital Twins, Digital Thread, AI/ML, and others. While this is not easy, the good news is that there are some proven technologies from various companies that help overcome these challenges. For example, HiveMQ offers a product called Data Hub, which provides an integrated policy and data transformation engine that validates, enforces, and manipulates data in motion to ensure data integrity, quality, and governance across the deployment. Another framework that enables robust data management is Unified Namespace (UNS) which provides a single source of truth for all of the organization's business data. The HiveMQ MQTT platform offers a very powerful UNS framework.
Automation
Automation in manufacturing involves the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. It encompasses a wide range of applications from simple repetitive tasks to complex processes involving advanced robotics and artificial intelligence. Given organizational challenges in manufacturing to plug gaps in workforces, combined with other challenges like component shortages, supply chain disruptions and the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, embracing automation is more important than ever. When asked about their biggest automation challenges in 2024, 29% of the manufacturers mentioned building a business case being the biggest challenge followed by case study and implementation (Fig. 3).
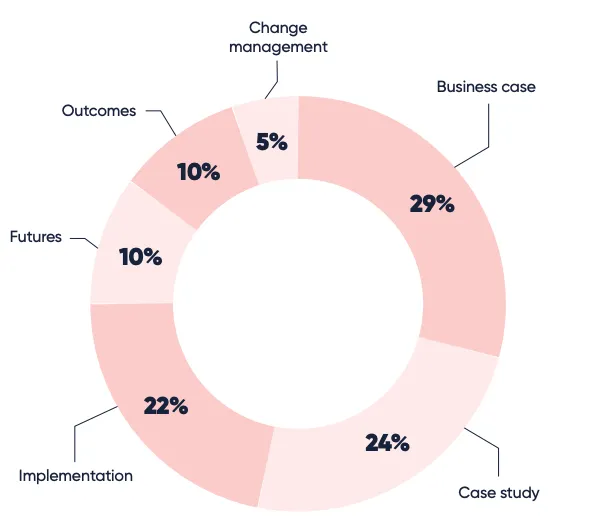 Fig 3: What are some of the challenges with automation in manufacturing?
Fig 3: What are some of the challenges with automation in manufacturing?
There are many ways to overcome some of the challenges with automation. One way is to start automation projects small, based on a true business case, so that the initial investment is low and building ROI would be straightforward. Another way is to incorporate a proper data management platform like HiveMQ combined with robust data governance processes, workforce training, and skill development.
Cybersecurity
Digital transformation is key to the prosperity of manufacturing. However, digital transformation heralds a new era of connectivity which brings with it rising levels of cyber vulnerability. Manufacturing has now overtaken financial services as the most cyber-attacked industry. Unlike the consumer space, manufacturing, a sector that is still in the preliminary stages of digital transformation, is not fully aware of the dangers that can be ushered through the doors of the plant or factory with the deployment of emerging, digital, connected technology. When asked about where the perceived challenge for cyber attacks will come from, an overwhelming 50% responded that it is from IIoT and connected devices (Fig. 4).
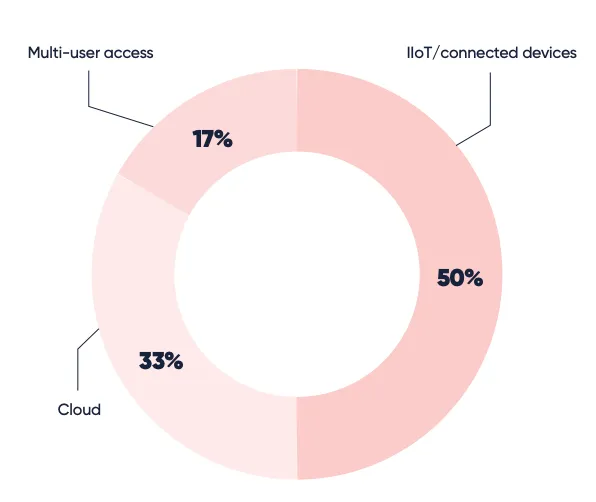 Fig. 4: What are some of the perceived challenges for Cybersecurity manufacturing?
Fig. 4: What are some of the perceived challenges for Cybersecurity manufacturing?
This is not surprising given the reservations that OT folks have for IIoT and Cloud, especially on the cybersecurity front. There are a lot of methods available from various vendors to help overcome these cybersecurity challenges. HiveMQ, for example, offers a lot of security features to help overcome security risk for data in motion and at rest. This includes native TLS/SSL encryption support for increased performance, support from simple username/password to fine-grained RBAC, and others (Fig. 5).
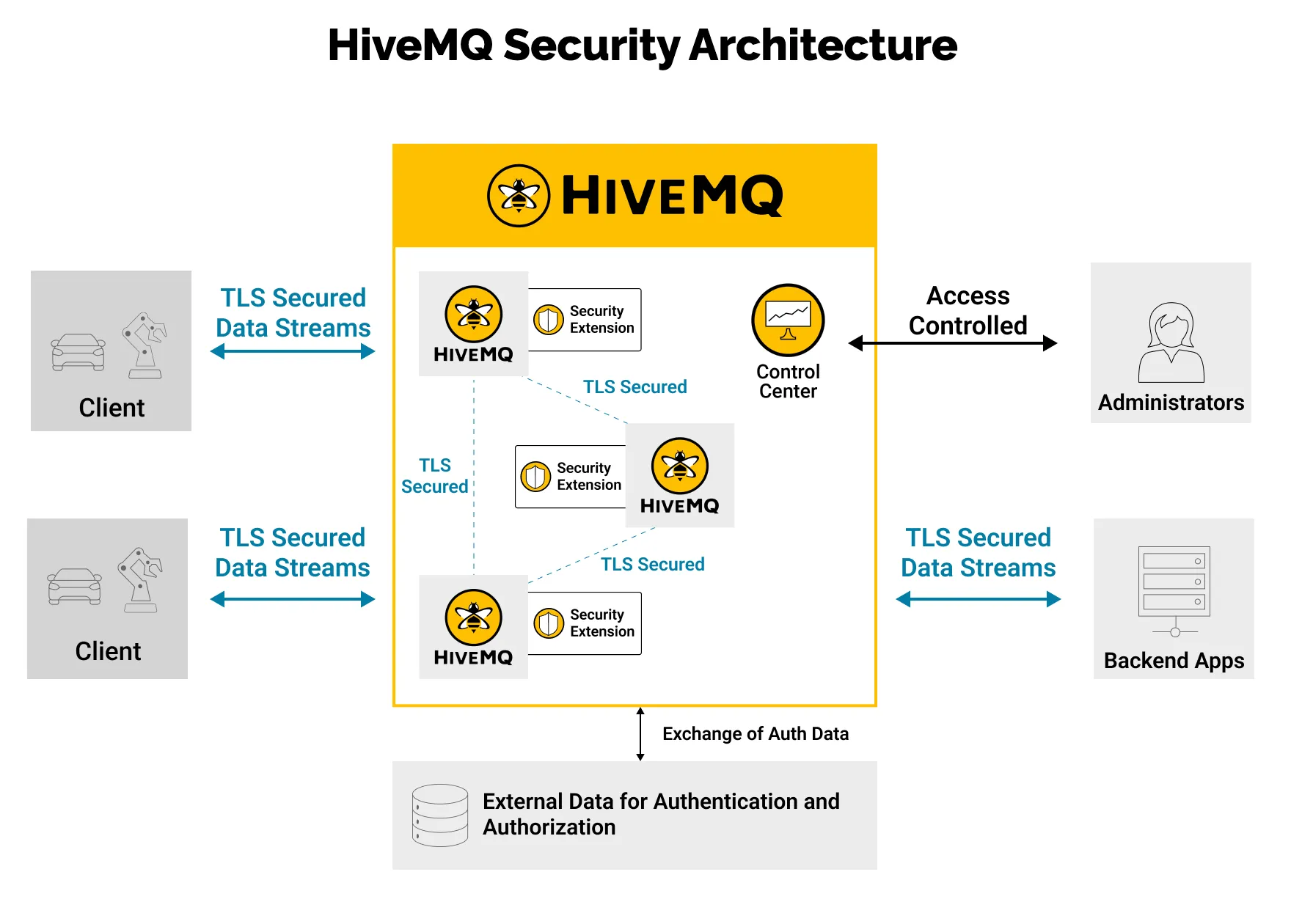 Fig. 5: HiveMQ security architecture
Fig. 5: HiveMQ security architecture
Along with cybersecurity, the other area of concern is compliance in regulated industries and data privacy in areas like the EU which have strict data privacy laws. The solution should be able to address this.
HiveMQ, for example, offers SOC 2 Type 1 and SOC 2 Type 2 compliance, GDPR compliance, and ISO/IEC 27001 standard of excellence for information security management systems.
Conclusion
The adoption of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing is a transformative journey that promises to revolutionize the sector through advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, big data analytics, and automation. However, this transformation is influenced by a multitude of factors that manufacturers must carefully consider to ensure successful implementation and realization of benefits. Effective data management is essential for leveraging the vast amounts of information generated by connected devices, and robust cybersecurity measures are critical to protect sensitive data and systems from cyber threats. HiveMQ can address the data and cybersecurity challenges by consolidating data, providing effective data management, and offering effective security measures. Download HiveMQ software and try us for free. Additionally, book a demo if you want to learn more.

Ravi Subramanyan
Ravi Subramanyan, Director of Industry Solutions, Manufacturing at HiveMQ, has extensive experience delivering high-quality products and services that have generated revenues and cost savings of over $10B for companies such as Motorola, GE, Bosch, and Weir. Ravi has successfully launched products, established branding, and created product advertisements and marketing campaigns for global and regional business teams.
