UNS for Enabling Resilience and Agility in Shop-Floor Scheduling
In industrial manufacturing, variability is the rule rather than the exception. Fluctuating demand, equipment breakdowns, supply chain disruptions, and labor shortages all contribute to the complexity of running a production facility. For plant managers, the challenge lies in maintaining optimal production levels in this unpredictable environment.
Traditional scheduling methods, which rely heavily on manual input and static algorithms, often fail to address the intricacies of a dynamic manufacturing process. They typically lack the speed and flexibility needed to react to unexpected events or optimize resources in real time. As a result, plant managers encounter unnecessary inefficiencies, miss deadlines, and face rising costs.
To resolve these challenges, many manufacturers turn to scheduling optimization—a sophisticated approach that leverages advanced algorithms, data analytics, and system integration to streamline production and maximize output. While some ERP platforms offer scheduling capabilities, they often lack the depth and granularity needed for comprehensive scheduling optimization. Consequently, many organizations opt for Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) software. APS focuses on achieving the ideal balance among multiple objectives, such as reducing setup times, lowering inventory levels, and meeting customer deadlines.
However, APS systems reach their full potential only when they are digitally integrated with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). Such integration streamlines data exchange, boosts agility, cuts costs, and provides real-time visibility across the production ecosystem. Unfortunately, many manufacturing operations still rely on spreadsheets and manual methods, limiting the advantages of end-to-end digitalization.
By introducing a Unified Namespace (UNS) as the hub for real-time data exchange—including work order status, machine availability, demand fluctuations, breakdowns, supply chain issues, and labor constraints—organizations can tap into a standard, open, and decoupled architecture driven by MQTT. As we will explore, this UNS-based approach paves the way for seamless APS-ERP-MES connectivity, driving efficient and fully digitalized manufacturing processes.
Challenges of Shop-Floor Scheduling with Digitally Disconnected APS Systems
When it comes down to real-world execution, the minute-by-minute decisions made on the shop floor are what truly drive future gains in efficiency. While high-level production planning shapes the bigger picture, it is the fine-grained, day-to-day adjustments that foster the resilience and adaptability needed for modern manufacturing.
Below are some of the common obstacles manufacturers face when their Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) systems lack seamless digital integration with other enterprise platforms.
Coordinating Multiple Resources
Many products require more than just a single machine or workstation to complete. In some cases, an item might need to pass through multiple pieces of equipment—or even require specialized labor—at precisely coordinated times. Without a connected APS system, tracking resource availability and timing across different workstations becomes cumbersome, leading to production delays, idle equipment, or suboptimal use of skilled personnel.
Complex Product Mixes and Regulatory Constraints
Manufacturers frequently handle products that vary significantly in terms of ingredients, formulas, or regulatory requirements. This is especially apparent with items that include allergens, must adhere to religious dietary rules, or fall under stringent standards like the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA). A disconnected APS solution often struggles to account for these specialized conditions in real time, increasing the likelihood of scheduling conflicts, compliance risks, or the need for unplanned changeovers.
Heightened Administrative Burden
When APS data is not seamlessly shared with systems like ERP and MES, planning teams are forced to juggle spreadsheets and compile information manually. This duplicative effort not only drains time and energy but also raises the chance of transcription errors and outdated data. The ripple effect can be felt across procurement, inventory management, and production control, where decisions hinge on accurate and timely information.
Limited Time for Proactive Planning
Because disconnected systems do not provide updates in real time, planners often remain in the dark about sudden changes on the shop floor—such as equipment failures or unexpected variations in production speed. This lack of up-to-date insights leaves minimal room for proactive scheduling adjustments. Consequently, managers are left reacting to issues rather than anticipating them, undermining efficiency and leading to unnecessary downtime.
Requirements for Resilient and Agile Shop-Floor Scheduling
Rapidly adapting to external pressures and making decisions that directly affect on-time delivery hinges on having up-to-date, accurate data. If your team cannot immediately see what is happening on the shop floor or within the supply chain, then it is nearly impossible to respond in time to keep production on track.
A digitally integrated scheduling system that connects to both ERP and MES platforms addresses key questions: Which machines should be used next? Who is going to operate them? Do we have the necessary materials right now? To answer these questions accurately, data from all relevant sources must continuously feed into your scheduling system, ensuring granular, real-time visibility.
Collecting data for scheduling purposes is only half the equation. The other critical factor is the ability to visualize and act on the information coming from your APS. Working with multiple spreadsheets makes rapid responses difficult. Instead, adopting a standardized interface and unified data model—like the one provided by the Unified Namespace data management strategy—consolidates all critical information into one readily accessible location, enabling faster and more effective decision-making.
UNS Framework for Real-Time Shop-Floor Scheduling
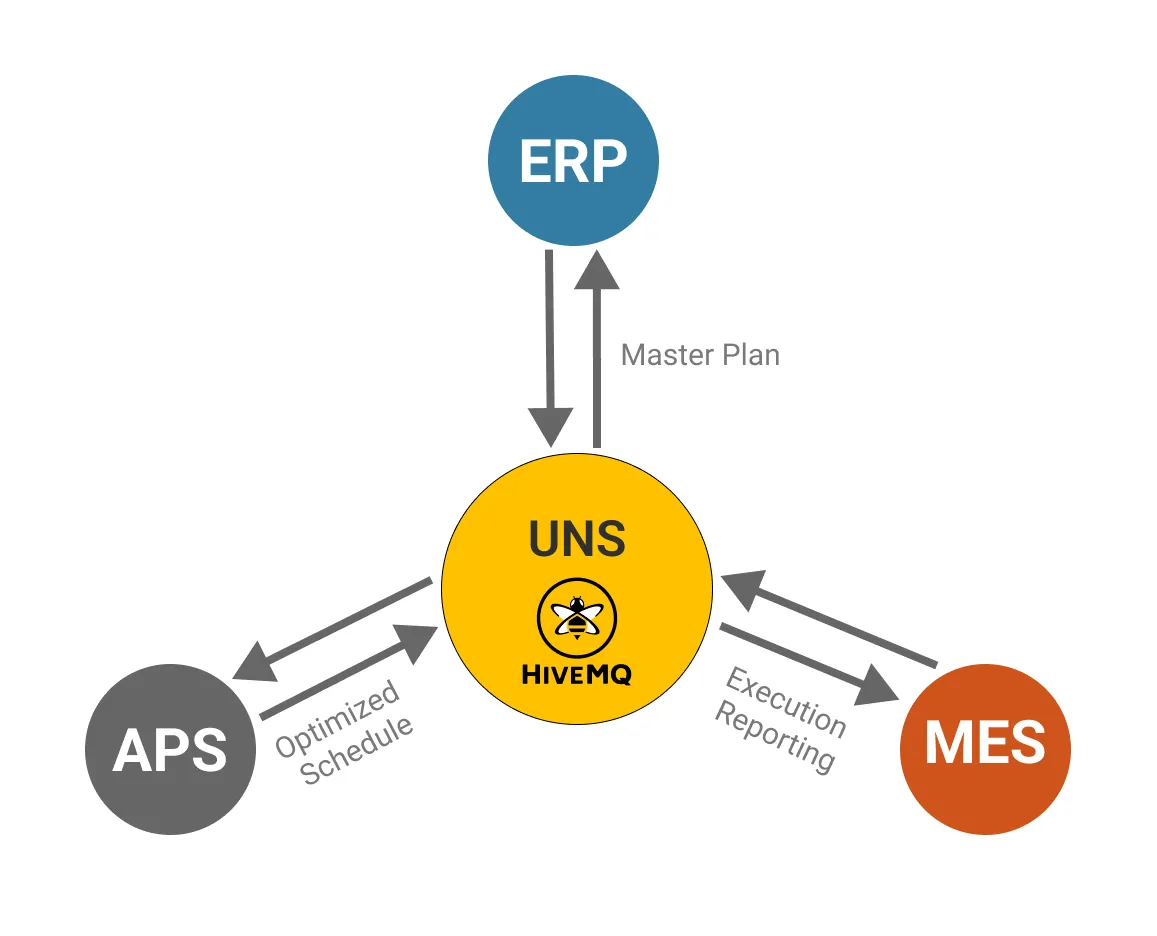
A Unified Namespace (UNS) provides a resilient, agile way to manage shop-floor scheduling by functioning as an open, standardized hub where Planning, Scheduling, and Execution systems continuously exchange data. At the heart of this approach, the Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) system subscribes to ERP order data on the UNS. Whenever new or updated orders come in, the APS leverages this real-time information to optimize the production sequence based on key performance criteria—such as on-time delivery, minimal setup, and proper labor allocation.
Once the APS has recalculated the optimal schedule (taking into account factors like machine availability, lead times, and priority), it publishes the revised or newly created schedule back to the UNS. The Manufacturing Execution System (MES) then executes orders according to this schedule. Because all parties use a single, shared data framework, there is a continuous feedback loop among the ERP, APS, and MES, ensuring that everyone has the most current information to make timely, well-informed decisions.
Below is an example Namespace for exchanging information between ERP, APS and MES through the UNS.
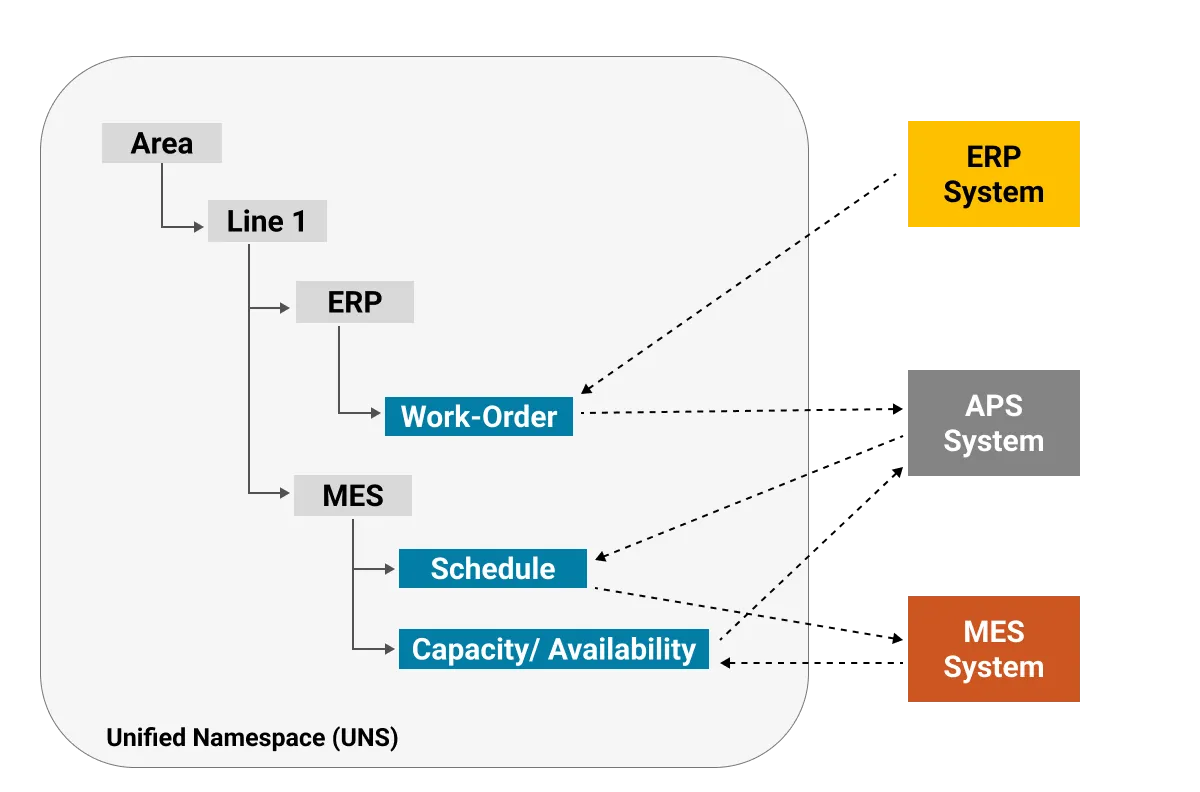 Below are examples of how the UNS framework leads to improved shop-floor scheduling outcomes.
Below are examples of how the UNS framework leads to improved shop-floor scheduling outcomes.
Faster Scheduling (From Hours to Seconds)
By having all relevant order, machine, and workforce data available in a common namespace, the APS system can dynamically incorporate changes and recalculate schedules almost instantly. In traditional siloed environments, this process could take hours due to manual data collection, spreadsheet updates, and delays from system-to-system synchronization. The UNS removes these bottlenecks, making rapid schedule updates the norm.
Enhanced Communication Across Departments
With the Unified Namespace, planners, supervisors, and operators all have access to the same real-time data set. This eliminates the need to pass around spreadsheets or email updates. Any change in orders, production progress, or resource availability is automatically reflected in the UNS, keeping every stakeholder on the same page and minimizing miscommunication.
Quicker Response to Expedited Orders, Changes, and Capacity Requests
Because the APS continuously monitors up-to-the-minute data through the UNS, it can immediately detect and respond to sudden changes—such as a priority shift in production or an unexpected jump in capacity needs. Instead of waiting on manual updates or departmental handoffs, the system instantly reads the event from the UNS, recalculates the schedule, and publishes a new plan. This rapid response capability helps maintain on-time delivery and adapt to shifting priorities without costly delays.
Conclusion
Keeping production on track in today’s volatile manufacturing environment requires more than just advanced software—it demands interoperable connectivity for real-time decision-making. A UNS offers exactly that: a single source of truth for real-time events that enables orchestration of complex scheduling decisions.
By shifting away from fragmented tools and manual coordination, manufacturers can create a more responsive and efficient operation. With ERP, APS, and MES systems all plugged into a shared, event-driven data backbone, teams gain the visibility and agility they need to swiftly adapt to unexpected changes. Stay tuned to the HiveMQ blog as I share many more use cases in upcoming posts.

Kudzai Manditereza
Kudzai is a tech influencer and electronic engineer based in Germany. As a Sr. Industry Solutions Advocate at HiveMQ, he helps developers and architects adopt MQTT and HiveMQ for their IIoT projects. Kudzai runs a popular YouTube channel focused on IIoT and Smart Manufacturing technologies and he has been recognized as one of the Top 100 global influencers talking about Industry 4.0 online.
